Definition[edit]
Pearson's correlation coefficient is the covariance of the two variables divided by the product of their standard deviations. The form of the definition involves a "product moment", that is, the mean (the first moment about the origin) of the product of the mean-adjusted random variables; hence the modifier product-moment in the name.
For a population[edit]
Pearson's correlation coefficient when applied to a population is commonly represented by the Greek letter ρ (rho) and may be referred to as the population correlation coefficient or the population Pearson correlation coefficient. The formula for ρ[7] is:
-
- where:
 is the covariance
is the covariance is the standard deviation of
is the standard deviation of 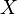
- where:
The formula for ρ can be expressed in terms of mean and expectation. Since
Then the formula for ρ can also be written as
-
- where:
 and
and  are defined as above
are defined as above is the mean of
is the mean of 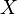
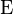 is the expectation.
is the expectation.
- where:
The formula for ρ can be expressed in terms of uncentered moments. Since
Then the formula for ρ can also be written as
For a sample[edit]
Pearson's correlation coefficient when applied to a sample is commonly represented by the letter r and may be referred to as the sample correlation coefficient or the sample Pearson correlation coefficient. We can obtain a formula for r by substituting estimates of the covariances and variances based on a sample into the formula above. So if we have one dataset {x1,...,xn} containing n values and another dataset {y1,...,yn} containing n values then that formula for r is:
-
- where:
-
 are defined as above
are defined as above (the sample mean); and analogously for
(the sample mean); and analogously for 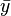
Rearranging gives us this formula for r:
-
- where:
-
 are defined as above
are defined as above- This formula suggests a convenient single-pass algorithm for calculating sample correlations, but, depending on the numbers involved, it can sometimes be numerically unstable.
Rearranging again gives us this[7] formula for r:
-
- where:
-
 are defined as above
are defined as above
An equivalent expression gives the formula for r as the mean of the products of the standard scores as follows:
-
- where
-
 are defined as above, and
are defined as above, and  are defined below
are defined below is the standard score (and analogously for the standard score of y)
is the standard score (and analogously for the standard score of y)
Alternative formulae for r are also available. One can use the following formula for r:
-
- where:
-
 are defined as above and:
are defined as above and: (the sample standard deviation); and analogously for sy
(the sample standard deviation); and analogously for sy
private static final double ZERO = 0.0d;int n;double[] x;double[] y;public PearsonCorrelation(Dataset ds, Item iA, Item iB) {double aAvgR = iA.getAverageRating();double bAvgR = iB.getAverageRating();Integer[] uid = Item.getSharedUserIds(iA, iB);n = uid.length;x = new double[n];y = new double[n];User u;double urA=0;double urB=0;for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {u = ds.getUser(uid[i]);urA = u.getItemRating(iA.getId()).getRating();urB = u.getItemRating(iB.getId()).getRating();x[i] = urA - aAvgR;y[i] = urB - bAvgR;}}public PearsonCorrelation(double[] x, double[] y) throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException {if (x.length != y.length) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Arrays x and y should have the same length!");}n = x.length;//System.out.print("N="+n);this.x = x;this.y = y;}public double calculate() {if( n == 0) {return 0.0;}double rho=0.0d;double avgX = getAverage(x);double avgY = getAverage(y);double sX = getStdDev(avgX,x);double sY = getStdDev(avgY,y);double xy=0;for (int i=0; i < n; i++) {xy += (x[i]-avgX)*(y[i]-avgY);}//No variation -- all points have the same values for either X or Y or bothif( sX == ZERO || sY == ZERO) {double indX = ZERO;double indY = ZERO;for (int i=1; i < n; i++) {indX += (x[0]-x[i]);indY += (y[0]-y[i]);}if (indX == ZERO && indY == ZERO) {// All points refer to the same value// This is a degenerate case of correlationreturn 1.0;} else {//Either the values of the X vary or the values of Yif (sX == ZERO) {sX = sY;} else {sY = sX;}}}rho = xy / (n*(sX*sY));return rho;}private double getAverage(double[] v) {double avg=0;for (double xi : v ) {avg += xi;}avg = avg/v.length;//System.out.print("Average: "+avg);return avg;}private double getStdDev(double m, double[] v) {double sigma=0;for (double xi : v ) {sigma += (xi - m)*(xi - m);}sigma = sigma / v.length;//System.out.print("StdDev: "+Math.sqrt(sigma));return Math.sqrt(sigma);}cs
- Programming Collective Intelligence
public double sim_pearson (Map < String, Map < String, Double >> personalRate, String person1, String person2) {Map<String, Double> Si = new HashMap<String, Double>();double result = 0;double sumP1 = 0;double sumP2 = 0;double sumP1Sq = 0 ;double sumP2Sq = 0 ;double pSum = 0;double pScore = 0 ;double num = 0;double den = 0 ;for (Map.Entry<String, Double> item : personalRate.get(person1).entrySet()) {for (Map.Entry<String, Double> item2 : personalRate.get(person2).entrySet()) {if (item.getKey().equals(item2.getKey())) {Si.put(item.getKey(), 1.0);}}}for ( Map.Entry<String,Double> matchedItem : Si.entrySet()) {sumP1 += personalRate.get(person1).get(matchedItem.getKey());sumP2 += personalRate.get(person2).get(matchedItem.getKey());sumP1Sq += Math.pow(personalRate.get(person1).get(matchedItem.getKey()), 2);sumP2Sq += Math.pow(personalRate.get(person2).get(matchedItem.getKey()), 2);pSum += (personalRate.get(person1).get(matchedItem.getKey())*personalRate.get(person2).get(matchedItem.getKey()));}num = pSum-(sumP1*sumP2/Si.size());den = Math.sqrt((sumP1Sq - Math.pow(sumP1 ,2)/Si.size())*(sumP2Sq - Math.pow(sumP2, 2)/Si.size()));if (den==0) result = 0;else result = num/den;return result;}cs

![\operatorname{cov}(X,Y) = \operatorname{E}[(X-\mu_X)(Y-\mu_Y)]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/math/8/5/e/85eb69fa2d810acdd879236a624c927d.png)
![\rho_{X,Y}=\frac{\operatorname{E}[(X-\mu_X)(Y-\mu_Y)]}{\sigma_X\sigma_Y}](https://upload.wikimedia.org/math/e/0/1/e0150d5feea4091277abdcbd9db35fc9.png)
![\mu_X=\operatorname{E}[X]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/math/2/1/3/213ddf84ba1cc6977c32c55298633f79.png)
![\mu_Y=\operatorname{E}[Y]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/math/5/0/7/507f97ca0759fff54ce4de46a70b4301.png)
![\sigma_X^2=\operatorname{E}[(X-\operatorname{E}[X])^2]=\operatorname{E}[X^2]-\operatorname{E}[X]^2](https://upload.wikimedia.org/math/9/1/4/9146607a529c5827a45c1ec27005f85e.png)
![\sigma_Y^2=\operatorname{E}[(Y-\operatorname{E}[Y])^2]=\operatorname{E}[Y^2]-\operatorname{E}[Y]^2](https://upload.wikimedia.org/math/5/7/d/57db9bf0e1ab9915656ae72f890e8017.png)
![\operatorname{E}[(X-\mu_X)(Y-\mu_Y)]=\operatorname{E}[(X-\operatorname{E}[X])(Y-\operatorname{E}[Y])]=\operatorname{E}[XY]-\operatorname{E}[X]\operatorname{E}[Y],\,](https://upload.wikimedia.org/math/4/3/3/433542b21e76326cc35511b216b2b6e7.png)
![\rho_{X,Y}=\frac{\operatorname{E}[XY]-\operatorname{E}[X]\operatorname{E}[Y]}{\sqrt{\operatorname{E}[X^2]-\operatorname{E}[X]^2}~\sqrt{\operatorname{E}[Y^2]- \operatorname{E}[Y]^2}}.](https://upload.wikimedia.org/math/3/a/8/3a8fd48ed9d34d02cb87f2604dc50c50.png)

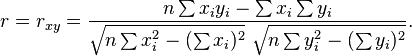



댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기